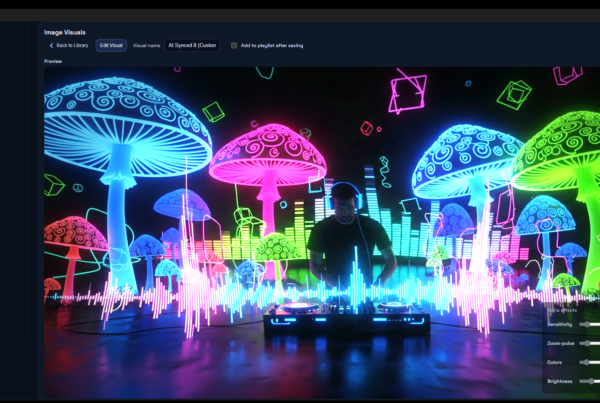
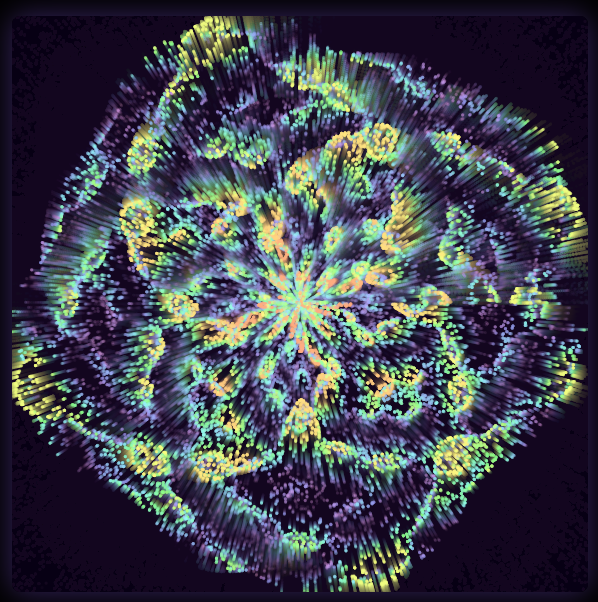
Audio responsive visualizers have become increasingly popular in recent years as a means of adding a visual element to music or other audio. These visualizers can take many forms, from simple graphic equalizers to complex 3D animations. In this article, we will explore the different things you can do with an audio responsive visualizer, including their use in music production, live performances, and art installations.
Music Production
One of the most common uses for audio responsive visualizers is in music production. By syncing the visualizer to the music, producers can get a better understanding of the sound they are creating. For example, a graphic equalizer can be used to show the levels of different frequencies in the music. This can help producers identify any problem areas that need to be addressed.
Visualizers can also be used to create music videos. By syncing the visuals to the music, producers can create stunning visuals that are synchronized to the beat. This can create a powerful and immersive experience for the viewer.
Live Performances
Audio responsive visualizers are also commonly used in live performances. By syncing the visuals to the music, performers can create a more engaging and immersive experience for the audience. This can be done through the use of projection mapping, LED screens, or other visual effects.
Projection mapping is a technique that involves projecting images or animations onto a physical object or surface. This can be used to create dynamic and immersive visuals that are synced to the music. For example, a DJ may project visuals onto a large sphere or cube that is synced to the beat of the music.
LED screens are another common way to display audio responsive visuals during live performances. These screens can be used to display a variety of visuals, from simple graphic equalizers to complex 3D animations. LED screens are often used in larger venues, such as music festivals or stadium shows.
Art Installations
Audio responsive visualizers are also used in art installations. These installations can take many forms, from interactive installations to immersive environments. For example, an artist may create an installation that uses audio responsive visuals to create a sensory experience for the viewer.
Interactive installations allow the viewer to interact with the audio responsive visuals in some way. This could be through the use of sensors or other input devices. For example, an installation may use a microphone to pick up the viewer’s voice and then use audio responsive visuals to create a unique and dynamic display.
Immersive environments are installations that are designed to completely immerse the viewer in a sensory experience. Audio responsive visuals can be used to create immersive environments by syncing the visuals to the music or other audio. This can create a powerful and emotional experience for the viewer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, audio responsive visualizers have become an important part of music production, live performances, and art installations. By syncing the visuals to the music or other audio, these visualizers can create stunning and immersive experiences for the viewer. Whether you are a music producer, performer, or artist, there are many different things you can do with an audio responsive visualizer. From simple graphic equalizers to complex 3D animations, the possibilities are endless.